Effect of iron and magnetite nanoparticles on the binding of cadmium and lead ions by humic acids
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24852/2411-7374.2024.1.84.92Keywords:
sorption, lead, cadmium, iron, humic acidsAbstract
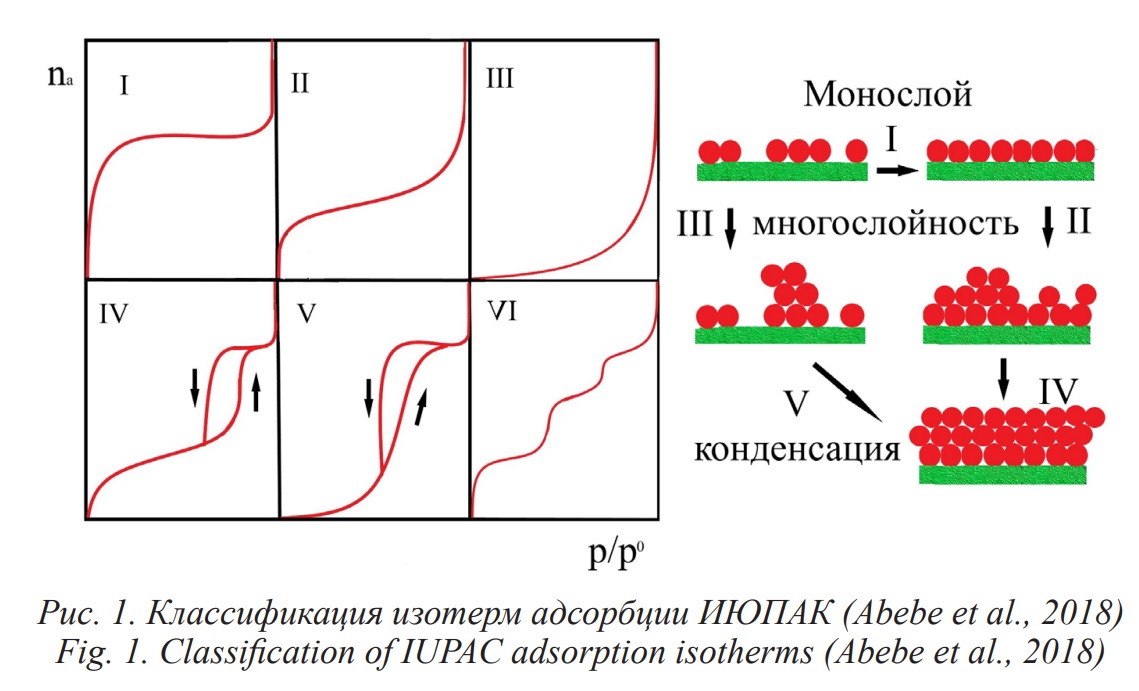
The article examines the influence of iron nanoparticles (80±5 nm) and magnetite (width from 50 nm to 80 nm and height from 4 nm to 10 nm) on the adsorption of toxic lead and cadmium ions from nitrate aqueous solutions on humic acids which isolated by alkaline extraction from brown coal from the Tyulgan deposit. Adsorption equilibria of cadmium and lead ions were studied in the concentration range from 0.1 mg/l to 1 mg/l at pH 6.0–6.5 on humic acids, iron and magnetite nanoparticles, as well as on iron nanoparticles in the presence of humic acids in mass ratio of 2:8 and on magnetite nanoparticles in the presence of humic acids at a mass ratio of 8:2, since at such ratios an increase in adsorption capacity is observed. Isotherms were described using the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Dubinin-Radushkevich equations. The kind of isotherms for the binding of cadmium ions on humic acids, iron nanoparticles, and magnetite corresponds to the first type of isotherms according to the IUPAC classification and is accompanied by the formation of a monomolecular layer, as well as during the adsorption of lead ions on humic acids and magnetite. On iron nanoparticles, the sorption isotherm of lead ions corresponds to the second type and assumes polymolecular adsorption. The sorption of cadmium and lead ions on iron and magnetite nanoparticles increases in the presence of humic acids, and the mechanism of physical adsorption changes from monomolecular to polymolecular, accompanied by a stronger adsorbate-adsorbate interaction than the adsorbate-adsorbent interaction. This is probably due to the formation of organomineral complexes, leading to charge redistribution and the formation of active adsorption centers on the surface of the sorbent
References
Antsiferova I. V. Istochniki postupleniya nanochastits v okruzhayushchuyu sredu [Sources of nanoparticles entering the environment] // Vestnik PNIPU. Mashinostroyeniye, materialovedeniye [Bulletin of PNIPU. Mechanical engineering, materials science]. 2012. No 2. P. 54‒66.
Mikhaylenko A.V., Ruban D. A. Zagryazneniye okruzhayushchey sredy kadmiyem pri ispol'zovanii solnechnykh batarey: sistemnyy obzor problemy [Environmental pollution with cadmium when using solar panels: a systematic review of the problem] // Otkhody i resursy [Waste and Resources] 2022. Vol. 9, No 3. URL: https://resources.today/PDF/10ECOR322.pdf. doi 10.15862/10ecor322.
Osipova E.A. Fiziko-khimicheskiye zakonomernosti svyazyvaniya ionov svintsa i kadmiya nanochastitsami zheleza i magnetita v prisutstvii guminovykh kislot [Physico-chemical regularities of binding of lead and cadmium ions by iron and magnetite nanoparticles in the presence of humic acids] // Izvestiya vysshikh uchebnykh zavedeniy. Ser.: khimiya i khimicheskaya tekhnologiya [News of higher educational institutions. Series: chemistry and chemical technology]. 2023. Vol. 66, No 9. P. 65‒70. doi: 10.6060/ivkkt.20236609.6788.
Perelomov L.V., Perelomova I.V., Lyovkin N.D., Muhina N.E., Korzini A., Andreoni V. Adsorbciya i okislenie soedinenij myshyaka mineralami zheleza i v biomineralnyh sictemah [Adsorption and oxidation of arsenic compounds by iron minerals and in biomineral systems] // Izvestiya Tulskogo universiteta. Estestvennye nauki [News of Tula University. Natural Sciences]. Tula, 2012. Iss. 3. P. 231‒240.
Chukubayeva A.N. Sorbiruyemost' svintsa na sapropele, burom ugle i vydelennykh iz nikh guminovykh kislotakh [Sorbability of lead on sapropel, brown coal and humic acids isolated from them] // Vestnik Kazakhstansko-Amerikanskogo svobodnogo universiteta [Bulletin of the Kazakh-American Free University]. 2008. No 3. P. 10‒14.
Sharapayev A. I., Muradova A. G., Yurtov Ye. V. Polucheniye magnitnykh nanochastits na osnove magnetita i farmatsevticheski priyemlemykh polimerov dlya MRT-diagnostiki [Preparation of magnetic nanoparticles based on magnetite and pharmaceutically acceptable polymers for MRI diagnostics] // Uspekhi v khimii i khimicheskoy tekhnologii [Advances in chemistry and chemical technology]. 2012. No 7. P. 97‒100.
Shestova G.V., Livanov G.A., Ostapenko Yu.N., Ivanova T.M., Sizova K.V. Opasnost' khronicheskikh otravleniy svintsom dlya zdorov'ya naseleniya [The danger of chronic lead poisoning for public health] // Meditsina ekstremal'nykh situatsiy [Medicine of extreme situations]. 2012. No 4. P. 65‒76.
Shimanovskiy N.L., Kulakov V.N., Grigor'yeva Ye.Yu., Lipengol'ts A.A. Nanorazmernyye chastitsy oksida zheleza dlya diagnostiki i gipertermicheskoy terapii v onkologii [Nanosized particles of iron oxide for diagnostics and hyperthermic therapy in oncology] // Rossiyskiy bioterapevticheskiy zhurnal [Russian biotherapeutic journal]. 2011. No 2. P. 25‒32.
Yurin V.M., Molchan O.V. Nanomaterialy i rasteniya: vzglyad na problemu [Nanomaterials and plants: a look at the problem] // Trudy BGU [Proceedings of BSU]. 2015. Vol. 10, part 1. P. 9‒21.
Abebe B., Murthy H., Amare E. Summary on Adsorption and Photocatalysis for Pollutant Remediation: Mini Review // Journal of encapsulation and adsorption sciences. 2018. Vol. 8. Р. 225‒255. doi: 10.4236/jeas.2018.84012.
Talabi A.O., Kayode T.J. Groundwater pollution and remediation // journal of water resource and protection. 2019. Vol. 11, №1. P.1‒19. doi: 10.4236/jwarp.2019.111001.
Bondarenko L., Kahru A., Terekhova V., Dzhardimalieva G., Uchanov P., Kydralieva K. Effects of humic acids on the ecotoxicity of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and Fe-ions: impact of oxidation and aging // Nanomaterials. 2020. Vol. 10. 2011. doi:10.3390/nano10102011.
Ebrahiminezhad A., Zare-Hoseinabadi A., Sarmah A.K., Taghizadeh S., Ghasemi Y., Berenjian A. Plant-mediated synthesis and applications of iron nanoparticles // Molecular biotechnology. 2018. Vol. 60 (2). P. 154‒168. doi: 10.1007/s12033-017-0053-4.
Eyyubova E.J., Nagiyev Kh.J., Chiragov F.M. Adsorption study of Fe (III) on modified adsorbent: adsorption isotherms and kinetics // Sorption and chromatographic processes. 2022. Vol. 22, No 4. P. 433‒441. doi.org/10.17308/sorpchrom.2022.22/10597.
Galdames A., Ruiz-Rubio L., Orueta M., Sánchez-Arzalluz M., Vilas-Vilela J.L. Zero-valent iron nanoparticles for soil and groundwater remediation // International journal of environmental research and public health. 2020. Vol. 17, No 16. 5817. doi:10.3390/ijerph17165817.
Javadian H. Application of kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic models for the adsorption of Co(II) ions on polyaniline/polypyrrole copolymer nanofibers from aqueous solution // Journal of industrial and engineering chemistry. 2014. Vol. 20, iss. 6. P. 4233–4241. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.01.026.
Hansel C.M., La Force M.J., Fendorf S., Sutton S. Spatial and temporal association of As and Fe species on aquatic plant roots // Environmental science & technology. 2002. Vol. 36, iss. 9. P. 1988‒1994. doi:10.1021/es015647d.
Hui C., Zhang Y., Ni X., Cheng Q., Zhao Y., Zhao Y., Du L., Jiang H. Interactions of iron-based nanoparticles with soil dissolved organic matter: adsorption, aging, and effects on hexavalent chromium removal // Journal of hazard materials. 2021. Vol. 406. 124650. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124650.
Jiang W., Cai Q., Xu W., Yang M., Cai Y., Dionysiou D. D., O'Shea K. E. Cr (VI) adsorption and reduction by humic acid coated on magnetite // Environmental science & technology. 2014. Vol. 48, iss.14. P. 8078‒8085. doi: 10.1021/es405804m.
Karn B., Kuiken T., Otto M. Nanotechnology and in situ remediation: a review of the benefits and potential risks // Environmental health perspectives. 2009. Vol. 117, iss. 12. P. 1813‒1831. doi:10.1289/ehp.0900793.
Mesárošová M., Kozics K., Bábelová A., Regendová E., Pastorek M., Vnuková D., Buliaková B., Rázga F., Gábelová A. The role of reactive oxygen species in the genotoxicity of surface-modified magnetite nanoparticles // Toxicology letters. 2014. Vol. 226. P. 303–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.02.025.
Mueller N.C., Braun J.E., Bruns J., Černík M., Rissing P., Rickerby D.G., Nowack B. Application of nanoscale zero valent iron (NZVI) for groundwater remediation in Europe // Environmental science and pollution research. 2011. Vol. 19. P. 550‒558.
Němeček J., Lhotský O., Cajthaml T. Nanoscale zero-valent iron application for in situ reduction of hexavalent chromium and its effects on indigenous microorganism populations // Science of the total environment. 2014. Vol. 485‒486. P. 739–747. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.105.
Pelikh V., Salnikova E., Sizentsov A., Osipova E., Ponomareva P. PSXI-23 Study of cadmium cumulation in agricultural products taking its geochemical distribution into account // Journal of animal science. 2021. Vol. 99. P. 349‒349. doi: 10.1093/jas/skab235.640.
Piccinno F., Gottschalk F., Seeger S., Nowack B. Industrial production quantities and uses of ten engineered nanomaterials in Europe and the world // Journal of nanoparticle research. 2012. Vol. 14, iss. 9. 1109. doi: 10.1007/s11051-012-1109-9.
Sun J., Chillrud S.N., Mailloux B.J., Stute M., Singh R., Dong H., Lepre C.J., Bostick B.C. Enhanced and stabilized arsenic retention in microcosms through the microbial oxidation of ferrous iron by nitrate // Chemosphere. 2016. Vol. 144. P. 1106‒1115. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.09.045.
Sundman A., Byrne J. M., Bauer I., Menguy N., Kappler A. Interactions between magnetite and humic substances: redox reactions and dissolution processes // Geochemical transactions. 2018. Vol. 18. 6. doi.org/10.1186/s12932-017-0044-1.
Tilston E. L., Collins C. D., Mitchell G. R., Princivalle J., Shaw L. J. Nanoscale zerovalent iron alters soil bacterial community structure and inhibits chloroaromatic biodegradation potential in Aroclor 1242-contaminated soil // Environmental polluiont. 2013. Vol. 173. P. 38–46. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.09.018.
Vítková M., Puschenreiter M., Komárek M. Effect of nano zero-valent iron application on As, Cd, Pb, and Zn availability in the rhizosphere of metal(loid) contaminated soils // Chemosphere. 2018. Vol. 200. P. 217‒226. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.118.
Waalkes M.P. Cadmium carcinogenesis // Mutation research. 2003. Vol. 10. P. 107‒120. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2003.07.011.
Wu K., Su D., Liu J., Saha R., Wang J.P. Magnetic nanoparticles in nanomedicine: a review of recent advances // Nanotechnology. 2019. Vol. 30, No 50. 502003. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ab4241.
Xu J. K., Zhang F. F., Sun J. J., Sheng J., Wang F., Sun M. Bio and nanomaterials based on Fe3O4 // Molecules. 2014. Vol. 19, iss. 12. P. 21506-21528. doi: 10.3390/molecules191221506.
Yap C. K., Al-Mutairi K. A. Ecological-health risk assessments of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, and Zn) in aquatic sediments from the ASEAN-5 emerging developing countries: a review and synthesis // Biology. 2022. Vol. 11, iss. 1. 7. doi: 10.3390/biology11010007
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




